
안녕하세요. 오픈소스컨설팅 Playce Cloud팀에서 오픈스택 기술지원을 담당하고 있는 이광철입니다.
저는 오픈소스컨설팅에서 오픈스택 / 쿠버네티스 분야에서 활동을 하고 있으며, 대형 인프라를 설계하고 구축 하고있습니다.
우리가 잘 알다 시피 대형 인프라를 구축하고 운영하기위해서는 많은 관련 지식과 기술들이 필요합니다.
이중에서 특히 필요한 기술은 동일한 서비스를 하게되는 서버들의 설정을 빠르게 동시에 할 수 있어야 하고, 인프라 전체에 확산되어 있는 장애의 처리가 가능해야 합니다. 그리고 서버의 정보를 확인 하기 위해 2대이상 많게는 100대 이상의 서버를 컨트롤 할 수 있어야 하죠.
그렇다면 이 때 사용 할 수 있는 기술이 무엇이 있을까요?
대표적으로 Ansible과 Terraform이 있습니다. 많이 사용되는 만큼 공개된 배포 버전도 상당히 많이 있는데요.
오늘은 Ansible을 이용하여 제가 구축과 기술지원을 하고 있는 오픈스택을 쉽게 설치하고 유지보수 할 수 있게 도와주는 Kolla-Ansible에 대해 설명하고, 직접 OpenStack을 설치 하면서 개념과 활용을 알아보겠습니다.

그 중 제가 선택한 도구는 Kolla-Ansible이며, 지금부터 Kolla-Ansible에 대해서 살펴보도록 하겠습니다.
Docker 컨테이너를 사용하여 오픈스택을 배포하고 관리하기 위한 Ansible 플레이북입니다.
Kolla-Ansible의 상세 문서는 OpenStack의 문서 사이트에서 확인이 가능하고, 필요한 정보를 상세하게 얻을 수 있습니다. [OpenStack – Kolla-Ansible Documentation]
Kolla-Ansible 구성을 보여주기 위해 저는 아래와 같은 시스템 요구 사항을 기반으로 해당 문서가 작성되었습니다.
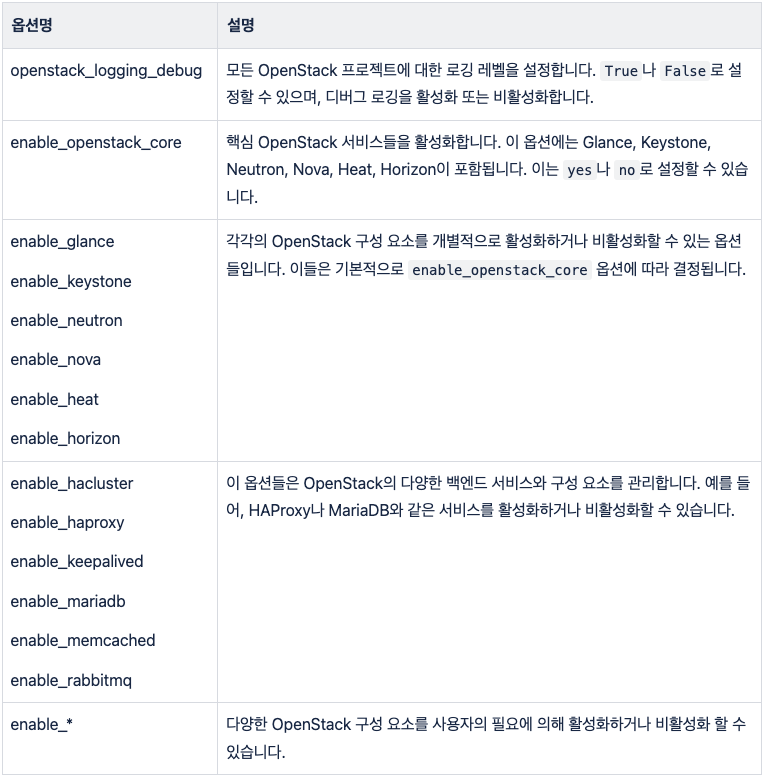
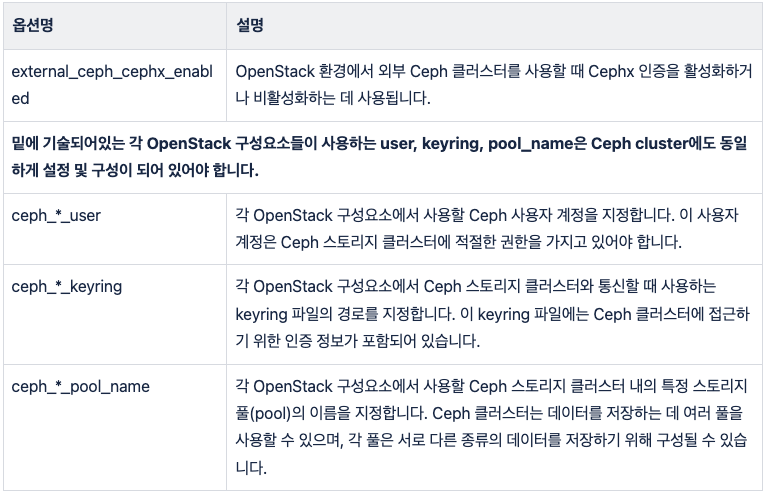
sudo dnf install git python3-devel libffi-devel gcc openssl-devel python3-libselinuxsudo apt install git python3-dev libffi-dev gcc libssl-devsudo apt install python3-venvpython3 -m venv /path/to/venv source /path/to/venv/bin/activatepip install -U pippip install 'ansible-core>=2.14,<2.16'pip install git+https://opendev.org/openstack/kolla-ansible@stable/2023.2/etc/kolla 디렉토리를 생성하고, Kolla-Ansible의 기본 구성 파일들을 해당 디렉토리로 복사합니다.mkdir -p /etc/kolla cp -r /path/to/venv/share/kolla-ansible/etc_examples/kolla/* /etc/kollaglobals.yml 파일을 편집하여 배포에 필요한 설정을 구성합니다. 여기에는 네트워크 설정, 사용할 OpenStack 버전, Docker 이미지 저장소 등이 포함됩니다. 기본 샘플 파일과 주요 옵션은 아래의 표를 참고하여 작성 합니다.---
# You can use this file to override _any_ variable throughout Kolla.
# Additional options can be found in the
# 'kolla-ansible/ansible/group_vars/all.yml' file. Default value of all the
# commented parameters are shown here, To override the default value uncomment
# the parameter and change its value.
###################
# Ansible options
###################
# This variable is used as the "filter" argument for the setup module. For
# instance, if one wants to remove/ignore all Neutron interface facts:
# kolla_ansible_setup_filter: "ansible_[!qt]*"
# By default, we do not provide a filter.
#kolla_ansible_setup_filter: "{{ omit }}"
# This variable is used as the "gather_subset" argument for the setup module.
# For instance, if one wants to avoid collecting facts via facter:
# kolla_ansible_setup_gather_subset: "all,!facter"
# By default, we do not provide a gather subset.
#kolla_ansible_setup_gather_subset: "{{ omit }}"
# Dummy variable to allow Ansible to accept this file.
workaround_ansible_issue_8743: yes
# This variable is used as "any_errors_fatal" setting for the setup (gather
# facts) plays.
# This is useful for weeding out failing hosts early to avoid late failures
# due to missing facts (especially cross-host).
# Do note this still supports host fact caching and it will not affect
# scenarios with all facts cached (as there is no task to fail).
#kolla_ansible_setup_any_errors_fatal: false
###############
# Kolla options
###############
# Valid options are [ COPY_ONCE, COPY_ALWAYS ]
#config_strategy: "COPY_ALWAYS"
# Valid options are ['centos', 'debian', 'rocky', 'ubuntu']
#kolla_base_distro: "rocky"
# Do not override this unless you know what you are doing.
#openstack_release: "2023.2"
# Docker image tag used by default.
#openstack_tag: "{{ openstack_release ~ openstack_tag_suffix }}"
# Suffix applied to openstack_release to generate openstack_tag.
#openstack_tag_suffix: ""
# Location of configuration overrides
#node_custom_config: "{{ node_config }}/config"
# This should be a VIP, an unused IP on your network that will float between
# the hosts running keepalived for high-availability. If you want to run an
# All-In-One without haproxy and keepalived, you can set enable_haproxy to no
# in "OpenStack options" section, and set this value to the IP of your
# 'network_interface' as set in the Networking section below.
#kolla_internal_vip_address: "10.10.10.254"
# This is the DNS name that maps to the kolla_internal_vip_address VIP. By
# default it is the same as kolla_internal_vip_address.
#kolla_internal_fqdn: "{{ kolla_internal_vip_address }}"
# This should be a VIP, an unused IP on your network that will float between
# the hosts running keepalived for high-availability. It defaults to the
# kolla_internal_vip_address, allowing internal and external communication to
# share the same address. Specify a kolla_external_vip_address to separate
# internal and external requests between two VIPs.
#kolla_external_vip_address: "{{ kolla_internal_vip_address }}"
# The Public address used to communicate with OpenStack as set in the public_url
# for the endpoints that will be created. This DNS name should map to
# kolla_external_vip_address.
#kolla_external_fqdn: "{{ kolla_external_vip_address }}"
# Optionally change the path to sysctl.conf modified by Kolla Ansible plays.
#kolla_sysctl_conf_path: /etc/sysctl.conf
##################
# Container engine
##################
# Valid options are [ docker, podman ]
#kolla_container_engine: docker
################
# Docker options
################
# Custom docker registry settings:
#docker_registry:
# Please read the docs carefully before applying docker_registry_insecure.
#docker_registry_insecure: "no"
#docker_registry_username:
# docker_registry_password is set in the passwords.yml file.
# Namespace of images:
#docker_namespace: "kolla"
# Docker client timeout in seconds.
#docker_client_timeout: 120
#docker_configure_for_zun: "no"
#containerd_configure_for_zun: "no"
#containerd_grpc_gid: 42463
###################
# Messaging options
###################
# Whether to enable TLS for oslo.messaging communication with RabbitMQ.
#om_enable_rabbitmq_tls: "{{ rabbitmq_enable_tls | bool }}"
# CA certificate bundle in containers using oslo.messaging with RabbitMQ TLS.
#om_rabbitmq_cacert: "{{ rabbitmq_cacert }}"
##############################
# Neutron - Networking Options
##############################
# This interface is what all your api services will be bound to by default.
# Additionally, all vxlan/tunnel and storage network traffic will go over this
# interface by default. This interface must contain an IP address.
# It is possible for hosts to have non-matching names of interfaces - these can
# be set in an inventory file per host or per group or stored separately, see
# http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/intro_inventory.html
# Yet another way to workaround the naming problem is to create a bond for the
# interface on all hosts and give the bond name here. Similar strategy can be
# followed for other types of interfaces.
#network_interface: "eth0"
# These can be adjusted for even more customization. The default is the same as
# the 'network_interface'. These interfaces must contain an IP address.
#kolla_external_vip_interface: "{{ network_interface }}"
#api_interface: "{{ network_interface }}"
#swift_storage_interface: "{{ network_interface }}"
#swift_replication_interface: "{{ swift_storage_interface }}"
#tunnel_interface: "{{ network_interface }}"
#dns_interface: "{{ network_interface }}"
#octavia_network_interface: "{{ api_interface }}"
# Configure the address family (AF) per network.
# Valid options are [ ipv4, ipv6 ]
#network_address_family: "ipv4"
#api_address_family: "{{ network_address_family }}"
#storage_address_family: "{{ network_address_family }}"
#swift_storage_address_family: "{{ storage_address_family }}"
#swift_replication_address_family: "{{ swift_storage_address_family }}"
#migration_address_family: "{{ api_address_family }}"
#tunnel_address_family: "{{ network_address_family }}"
#octavia_network_address_family: "{{ api_address_family }}"
#bifrost_network_address_family: "{{ network_address_family }}"
#dns_address_family: "{{ network_address_family }}"
# This is the raw interface given to neutron as its external network port. Even
# though an IP address can exist on this interface, it will be unusable in most
# configurations. It is recommended this interface not be configured with any IP
# addresses for that reason.
#neutron_external_interface: "eth1"
# Valid options are [ openvswitch, ovn, linuxbridge, vmware_nsxv, vmware_nsxv3, vmware_nsxp, vmware_dvs ]
# if vmware_nsxv3 or vmware_nsxp is selected, enable_openvswitch MUST be set to "no" (default is yes)
# Do note linuxbridge is *EXPERIMENTAL* in Neutron since Zed and it requires extra tweaks to config to be usable.
# For details, see: https://docs.openstack.org/neutron/latest/admin/config-experimental-framework.html
#neutron_plugin_agent: "openvswitch"
# Valid options are [ internal, infoblox ]
#neutron_ipam_driver: "internal"
# Configure Neutron upgrade option, currently Kolla support
# two upgrade ways for Neutron: legacy_upgrade and rolling_upgrade
# The variable "neutron_enable_rolling_upgrade: yes" is meaning rolling_upgrade
# were enabled and opposite
# Neutron rolling upgrade were enable by default
#neutron_enable_rolling_upgrade: "yes"
# Configure neutron logging framework to log ingress/egress connections to instances
# for security groups rules. More information can be found here:
# https://docs.openstack.org/neutron/latest/admin/config-logging.html
#enable_neutron_packet_logging: "no"
####################
# keepalived options
####################
# Arbitrary unique number from 0..255
# This should be changed from the default in the event of a multi-region deployment
# where the VIPs of different regions reside on a common subnet.
#keepalived_virtual_router_id: "51"
###################
# Dimension options
###################
# This is to provide an extra option to deploy containers with Resource constraints.
# We call it dimensions here.
# The dimensions for each container are defined by a mapping, where each dimension value should be a
# string.
# Reference_Docs
# https://docs.docker.com/config/containers/resource_constraints/
# eg:
# <container_name>_dimensions:
# blkio_weight:
# cpu_period:
# cpu_quota:
# cpu_shares:
# cpuset_cpus:
# cpuset_mems:
# mem_limit:
# mem_reservation:
# memswap_limit:
# kernel_memory:
# ulimits:
#####################
# Healthcheck options
#####################
#enable_container_healthchecks: "yes"
# Healthcheck options for Docker containers
# interval/timeout/start_period are in seconds
#default_container_healthcheck_interval: 30
#default_container_healthcheck_timeout: 30
#default_container_healthcheck_retries: 3
#default_container_healthcheck_start_period: 5
##################
# Firewall options
##################
# Configures firewalld on both ubuntu and centos systems
# for enabled services.
# firewalld should be installed beforehand.
# disable_firewall: "true"
# enable_external_api_firewalld: "false"
# external_api_firewalld_zone: "public"
#############
# TLS options
#############
# To provide encryption and authentication on the kolla_external_vip_interface,
# TLS can be enabled. When TLS is enabled, certificates must be provided to
# allow clients to perform authentication.
#kolla_enable_tls_internal: "no"
#kolla_enable_tls_external: "{{ kolla_enable_tls_internal if kolla_same_external_internal_vip | bool else 'no' }}"
#kolla_certificates_dir: "{{ node_config }}/certificates"
#kolla_external_fqdn_cert: "{{ kolla_certificates_dir }}/haproxy.pem"
#kolla_internal_fqdn_cert: "{{ kolla_certificates_dir }}/haproxy-internal.pem"
#kolla_admin_openrc_cacert: ""
#kolla_copy_ca_into_containers: "no"
#haproxy_backend_cacert: "{{ 'ca-certificates.crt' if kolla_base_distro in ['debian', 'ubuntu'] else 'ca-bundle.trust.crt' }}"
#haproxy_backend_cacert_dir: "/etc/ssl/certs"
##################
# Backend options
##################
#kolla_httpd_keep_alive: "60"
#kolla_httpd_timeout: "60"
#####################
# Backend TLS options
#####################
#kolla_enable_tls_backend: "no"
#kolla_verify_tls_backend: "yes"
#kolla_tls_backend_cert: "{{ kolla_certificates_dir }}/backend-cert.pem"
#kolla_tls_backend_key: "{{ kolla_certificates_dir }}/backend-key.pem"
#####################
# ACME client options
#####################
# A list of haproxy backend server directives pointing to addresses used by the
# ACME client to complete http-01 challenge.
# Please read the docs for more details.
#acme_client_servers: []
####################
# LetsEncrypt options
####################
# This option is required for letsencrypt role to work properly.
#letsencrypt_email: ""
####################
# LetsEncrypt certificate server options
####################
#letsencrypt_cert_server: "https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory"
# attempt to renew Let's Encrypt certificate every 12 hours
#letsencrypt_cron_renew_schedule: "0 */12 * * *"
################
# Region options
################
# Use this option to change the name of this region.
#openstack_region_name: "RegionOne"
# Use this option to define a list of region names - only needs to be configured
# in a multi-region deployment, and then only in the *first* region.
#multiple_regions_names: ["{{ openstack_region_name }}"]
###################
# OpenStack options
###################
# Use these options to set the various log levels across all OpenStack projects
# Valid options are [ True, False ]
#openstack_logging_debug: "False"
# Enable core OpenStack services. This includes:
# glance, keystone, neutron, nova, heat, and horizon.
#enable_openstack_core: "yes"
# These roles are required for Kolla to be operation, however a savvy deployer
# could disable some of these required roles and run their own services.
#enable_glance: "{{ enable_openstack_core | bool }}"
#enable_hacluster: "no"
#enable_haproxy: "yes"
#enable_keepalived: "{{ enable_haproxy | bool }}"
#enable_keystone: "{{ enable_openstack_core | bool }}"
#enable_mariadb: "yes"
#enable_memcached: "yes"
#enable_neutron: "{{ enable_openstack_core | bool }}"
#enable_nova: "{{ enable_openstack_core | bool }}"
#enable_rabbitmq: "{{ 'yes' if om_rpc_transport == 'rabbit' or om_notify_transport == 'rabbit' else 'no' }}"
#enable_outward_rabbitmq: "{{ enable_murano | bool }}"
# OpenStack services can be enabled or disabled with these options
#enable_aodh: "no"
#enable_barbican: "no"
#enable_blazar: "no"
#enable_ceilometer: "no"
#enable_ceilometer_ipmi: "no"
#enable_cells: "no"
#enable_central_logging: "no"
#enable_ceph_rgw: "no"
#enable_ceph_rgw_loadbalancer: "{{ enable_ceph_rgw | bool }}"
#enable_cinder: "no"
#enable_cinder_backup: "yes"
#enable_cinder_backend_hnas_nfs: "no"
#enable_cinder_backend_iscsi: "{{ enable_cinder_backend_lvm | bool }}"
#enable_cinder_backend_lvm: "no"
#enable_cinder_backend_nfs: "no"
#enable_cinder_backend_quobyte: "no"
#enable_cinder_backend_pure_iscsi: "no"
#enable_cinder_backend_pure_fc: "no"
#enable_cinder_backend_pure_roce: "no"
#enable_cloudkitty: "no"
#enable_collectd: "no"
#enable_cyborg: "no"
#enable_designate: "no"
#enable_destroy_images: "no"
#enable_etcd: "no"
#enable_fluentd: "yes"
#enable_freezer: "no"
#enable_gnocchi: "no"
#enable_gnocchi_statsd: "no"
#enable_grafana: "no"
#enable_grafana_external: "{{ enable_grafana | bool }}"
#enable_heat: "{{ enable_openstack_core | bool }}"
#enable_horizon: "{{ enable_openstack_core | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_blazar: "{{ enable_blazar | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_cloudkitty: "{{ enable_cloudkitty | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_designate: "{{ enable_designate | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_freezer: "{{ enable_freezer | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_heat: "{{ enable_heat | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_ironic: "{{ enable_ironic | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_magnum: "{{ enable_magnum | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_manila: "{{ enable_manila | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_masakari: "{{ enable_masakari | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_mistral: "{{ enable_mistral | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_murano: "{{ enable_murano | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_neutron_vpnaas: "{{ enable_neutron_vpnaas | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_octavia: "{{ enable_octavia | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_sahara: "{{ enable_sahara | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_senlin: "{{ enable_senlin | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_solum: "{{ enable_solum | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_tacker: "{{ enable_tacker | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_trove: "{{ enable_trove | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_vitrage: "{{ enable_vitrage | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_watcher: "{{ enable_watcher | bool }}"
#enable_horizon_zun: "{{ enable_zun | bool }}"
#enable_influxdb: "{{ enable_cloudkitty | bool and cloudkitty_storage_backend == 'influxdb' }}"
#enable_ironic: "no"
#enable_ironic_neutron_agent: "{{ enable_neutron | bool and enable_ironic | bool }}"
#enable_ironic_prometheus_exporter: "{{ enable_ironic | bool and enable_prometheus | bool }}"
#enable_iscsid: "{{ enable_cinder | bool and enable_cinder_backend_iscsi | bool }}"
#enable_kuryr: "no"
#enable_magnum: "no"
#enable_manila: "no"
#enable_manila_backend_generic: "no"
#enable_manila_backend_hnas: "no"
#enable_manila_backend_cephfs_native: "no"
#enable_manila_backend_cephfs_nfs: "no"
#enable_manila_backend_glusterfs_nfs: "no"
#enable_mariabackup: "no"
#enable_masakari: "no"
#enable_mistral: "no"
#enable_multipathd: "no"
#enable_murano: "no"
#enable_neutron_vpnaas: "no"
#enable_neutron_sriov: "no"
#enable_neutron_dvr: "no"
#enable_neutron_qos: "no"
#enable_neutron_agent_ha: "no"
#enable_neutron_bgp_dragent: "no"
#enable_neutron_provider_networks: "no"
#enable_neutron_segments: "no"
#enable_neutron_sfc: "no"
#enable_neutron_trunk: "no"
#enable_neutron_metering: "no"
#enable_neutron_infoblox_ipam_agent: "no"
#enable_neutron_port_forwarding: "no"
#enable_nova_serialconsole_proxy: "no"
#enable_nova_ssh: "yes"
#enable_octavia: "no"
#enable_octavia_driver_agent: "{{ enable_octavia | bool and neutron_plugin_agent == 'ovn' }}"
#enable_octavia_jobboard: "{{ enable_octavia | bool and 'amphora' in octavia_provider_drivers }}"
#enable_opensearch: "{{ enable_central_logging | bool or enable_osprofiler | bool or (enable_cloudkitty | bool and cloudkitty_storage_backend == 'elasticsearch') }}"
#enable_opensearch_dashboards: "{{ enable_opensearch | bool }}"
#enable_opensearch_dashboards_external: "{{ enable_opensearch_dashboards | bool }}"
#enable_openvswitch: "{{ enable_neutron | bool and neutron_plugin_agent != 'linuxbridge' }}"
#enable_ovn: "{{ enable_neutron | bool and neutron_plugin_agent == 'ovn' }}"
#enable_ovs_dpdk: "no"
#enable_osprofiler: "no"
#enable_placement: "{{ enable_nova | bool or enable_zun | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus: "no"
#enable_proxysql: "no"
#enable_redis: "no"
#enable_sahara: "no"
#enable_senlin: "no"
#enable_skyline: "no"
#enable_solum: "no"
#enable_swift: "no"
#enable_swift_s3api: "no"
#enable_tacker: "no"
#enable_telegraf: "no"
#enable_trove: "no"
#enable_trove_singletenant: "no"
#enable_venus: "no"
#enable_vitrage: "no"
#enable_watcher: "no"
#enable_zun: "no"
#############
# S3 options
#############
# Common options for S3 Cinder Backup and Glance S3 backend.
#s3_url:
#s3_bucket:
#s3_access_key:
#s3_secret_key:
##################
# RabbitMQ options
##################
# Options passed to RabbitMQ server startup script via the
# RABBITMQ_SERVER_ADDITIONAL_ERL_ARGS environment var.
# See Kolla Ansible docs RabbitMQ section for details.
# These are appended to args already provided by Kolla Ansible
# to configure IPv6 in RabbitMQ server.
# More details can be found in the RabbitMQ docs:
# https://www.rabbitmq.com/runtime.html#scheduling
# https://www.rabbitmq.com/runtime.html#busy-waiting
# The default tells RabbitMQ to always use two cores (+S 2:2),
# and not to busy wait (+sbwt none +sbwtdcpu none +sbwtdio none):
#rabbitmq_server_additional_erl_args: "+S 2:2 +sbwt none +sbwtdcpu none +sbwtdio none"
# Whether to enable TLS encryption for RabbitMQ client-server communication.
#rabbitmq_enable_tls: "no"
# CA certificate bundle in RabbitMQ container.
#rabbitmq_cacert: "/etc/ssl/certs/{{ 'ca-certificates.crt' if kolla_base_distro in ['debian', 'ubuntu'] else 'ca-bundle.trust.crt' }}"
#################
# MariaDB options
#################
# List of additional WSREP options
#mariadb_wsrep_extra_provider_options: []
#######################
# External Ceph options
#######################
# External Ceph - cephx auth enabled (this is the standard nowadays, defaults to yes)
#external_ceph_cephx_enabled: "yes"
# Glance
#ceph_glance_user: "glance"
#ceph_glance_keyring: "client.{{ ceph_glance_user }}.keyring"
#ceph_glance_pool_name: "images"
# Cinder
#ceph_cinder_user: "cinder"
#ceph_cinder_keyring: "client.{{ ceph_cinder_user }}.keyring"
#ceph_cinder_pool_name: "volumes"
#ceph_cinder_backup_user: "cinder-backup"
#ceph_cinder_backup_keyring: "client.{{ ceph_cinder_backup_user }}.keyring"
#ceph_cinder_backup_pool_name: "backups"
# Nova
#ceph_nova_keyring: "{{ ceph_cinder_keyring }}"
#ceph_nova_user: "nova"
#ceph_nova_pool_name: "vms"
# Gnocchi
#ceph_gnocchi_user: "gnocchi"
#ceph_gnocchi_keyring: "client.{{ ceph_gnocchi_user }}.keyring"
#ceph_gnocchi_pool_name: "gnocchi"
# Manila
#ceph_manila_user: "manila"
#ceph_manila_keyring: "client.{{ ceph_manila_user }}.keyring"
#############################
# Keystone - Identity Options
#############################
#keystone_admin_user: "admin"
#keystone_admin_project: "admin"
# Interval to rotate fernet keys by (in seconds). Must be an interval of
# 60(1 min), 120(2 min), 180(3 min), 240(4 min), 300(5 min), 360(6 min),
# 600(10 min), 720(12 min), 900(15 min), 1200(20 min), 1800(30 min),
# 3600(1 hour), 7200(2 hour), 10800(3 hour), 14400(4 hour), 21600(6 hour),
# 28800(8 hour), 43200(12 hour), 86400(1 day), 604800(1 week).
#fernet_token_expiry: 86400
# Whether or not to apply changes to service user passwords when services are
# reconfigured
#update_keystone_service_user_passwords: "true"
########################
# Glance - Image Options
########################
# Configure image backend.
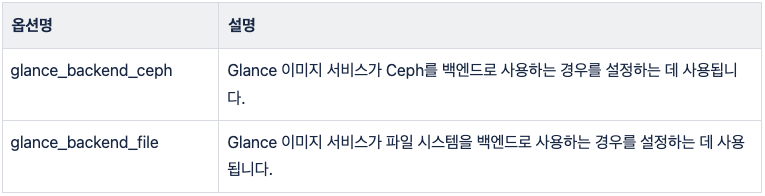
#glance_backend_ceph: "no"
#glance_backend_file: "yes"
#glance_backend_swift: "no"
#glance_backend_vmware: "no"
#glance_backend_s3: "no"
#enable_glance_image_cache: "no"
#glance_enable_property_protection: "no"
#glance_enable_interoperable_image_import: "no"
# Configure glance upgrade option.
# Due to this feature being experimental in glance,
# the default value is "no".
#glance_enable_rolling_upgrade: "no"
####################
# Glance S3 Backend
####################
#glance_backend_s3_url: "{{ s3_url }}"
#glance_backend_s3_bucket: "{{ s3_bucket }}"
#glance_backend_s3_access_key: "{{ s3_access_key }}"
#glance_backend_s3_secret_key: "{{ s3_secret_key }}"
####################
# Osprofiler options
####################
# valid values: ["elasticsearch", "redis"]
#osprofiler_backend: "elasticsearch"
##################
# Barbican options
##################
# Valid options are [ simple_crypto, p11_crypto ]
#barbican_crypto_plugin: "simple_crypto"
#barbican_library_path: "/usr/lib/libCryptoki2_64.so"
#################
# Gnocchi options
#################
# Valid options are [ file, ceph, swift ]
#gnocchi_backend_storage: "{% if enable_swift | bool %}swift{% else %}file{% endif %}"
# Valid options are [redis, '']
#gnocchi_incoming_storage: "{{ 'redis' if enable_redis | bool else '' }}"
################################
# Cinder - Block Storage Options
################################
# Enable / disable Cinder backends
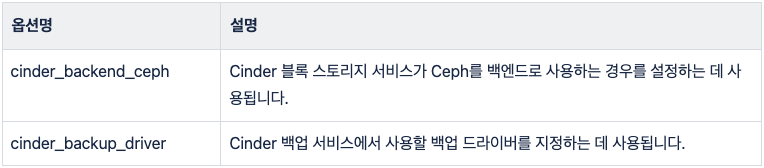
#cinder_backend_ceph: "no"
#cinder_backend_vmwarevc_vmdk: "no"
#cinder_backend_vmware_vstorage_object: "no"
#cinder_volume_group: "cinder-volumes"
# Valid options are [ '', redis, etcd ]
#cinder_coordination_backend: "{{ 'redis' if enable_redis|bool else 'etcd' if enable_etcd|bool else '' }}"
# Valid options are [ nfs, swift, ceph, s3 ]
#cinder_backup_driver: "ceph"
#cinder_backup_share: ""
#cinder_backup_mount_options_nfs: ""
# Cinder backup S3 options
#cinder_backup_s3_url: "{{ s3_url }}"
#cinder_backup_s3_bucket: "{{ s3_bucket }}"
#cinder_backup_s3_access_key: "{{ s3_access_key }}"
#cinder_backup_s3_secret_key: "{{ s3_secret_key }}"
#######################
# Cloudkitty options
#######################
# Valid option is gnocchi
#cloudkitty_collector_backend: "gnocchi"
# Valid options are 'sqlalchemy' or 'influxdb'. The default value is
# 'influxdb', which matches the default in Cloudkitty since the Stein release.
# When the backend is "influxdb", we also enable Influxdb.
# Also, when using 'influxdb' as the backend, we trigger the configuration/use
# of Cloudkitty storage backend version 2.
#cloudkitty_storage_backend: "influxdb"
###################
# Designate options
###################
# Valid options are [ bind9 ]
#designate_backend: "bind9"
#designate_ns_record:
# - "ns1.example.org"
# Valid options are [ '', redis ]
#designate_coordination_backend: "{{ 'redis' if enable_redis|bool else '' }}"
########################
# Nova - Compute Options
########################
#nova_backend_ceph: "no"
# Valid options are [ qemu, kvm, vmware ]
#nova_compute_virt_type: "kvm"
# The number of fake driver per compute node
#num_nova_fake_per_node: 5
# The flag "nova_safety_upgrade" need to be consider when
# "nova_enable_rolling_upgrade" is enabled. The "nova_safety_upgrade"
# controls whether the nova services are all stopped before rolling
# upgrade to the new version, for the safety and availability.
# If "nova_safety_upgrade" is "yes", that will stop all nova services (except
# nova-compute) for no failed API operations before upgrade to the
# new version. And opposite.
#nova_safety_upgrade: "no"
# Valid options are [ none, novnc, spice ]
#nova_console: "novnc"
##############################
# Neutron - networking options
##############################
# Enable distributed floating ip for OVN deployments
#neutron_ovn_distributed_fip: "no"
# Enable DHCP agent(s) to use with OVN
#neutron_ovn_dhcp_agent: "no"
#############################
# Horizon - Dashboard Options
#############################
#horizon_backend_database: "{{ enable_murano | bool }}"
#############################
# Ironic options
#############################
# dnsmasq bind interface for Ironic Inspector, by default is network_interface
#ironic_dnsmasq_interface: "{{ network_interface }}"
# The following value must be set when enabling ironic, the value format is a
# list of ranges - at least one must be configured, for example:
# - range: 192.168.0.10,192.168.0.100
# See Kolla Ansible docs on Ironic for details.
#ironic_dnsmasq_dhcp_ranges:
# PXE bootloader file for Ironic Inspector, relative to /var/lib/ironic/tftpboot.
#ironic_dnsmasq_boot_file: "pxelinux.0"
# Configure ironic upgrade option, due to currently kolla support
# two upgrade ways for ironic: legacy_upgrade and rolling_upgrade
# The variable "ironic_enable_rolling_upgrade: yes" is meaning rolling_upgrade
# were enabled and opposite
# Rolling upgrade were enable by default
#ironic_enable_rolling_upgrade: "yes"
# List of extra kernel parameters passed to the kernel used during inspection
#ironic_inspector_kernel_cmdline_extras: []
# Valid options are [ '', redis, etcd ]
#ironic_coordination_backend: "{{ 'redis' if enable_redis|bool else 'etcd' if enable_etcd|bool else '' }}"
######################################
# Manila - Shared File Systems Options
######################################
# HNAS backend configuration
#hnas_ip:
#hnas_user:
#hnas_password:
#hnas_evs_id:
#hnas_evs_ip:
#hnas_file_system_name:
# CephFS backend configuration.
# External Ceph FS name.
# By default this is empty to allow Manila to auto-find the first FS available.
#manila_cephfs_filesystem_name:
# Gluster backend configuration
# The option of glusterfs share layout can be directory or volume
# The default option of share layout is 'volume'
#manila_glusterfs_share_layout:
# The default option of nfs server type is 'Gluster'
#manila_glusterfs_nfs_server_type:
# Volume layout Options (required)
# If the glusterfs server requires remote ssh, then you need to fill
# in 'manila_glusterfs_servers', ssh user 'manila_glusterfs_ssh_user', and ssh password
# 'manila_glusterfs_ssh_password'.
# 'manila_glusterfs_servers' value List of GlusterFS servers which provide volumes,
# the format is for example:
# - 10.0.1.1
# - 10.0.1.2
#manila_glusterfs_servers:
#manila_glusterfs_ssh_user:
#manila_glusterfs_ssh_password:
# Used to filter GlusterFS volumes for share creation.
# Examples: manila-share-volume-\\d+$, manila-share-volume-#{size}G-\\d+$;
#manila_glusterfs_volume_pattern:
# Directory layout Options
# If the glusterfs server is on the local node of the manila share,
# it’s of the format <glustervolserver>:/<glustervolid>
# If the glusterfs server is on a remote node,
# it’s of the format <username>@<glustervolserver>:/<glustervolid> ,
# and define 'manila_glusterfs_ssh_password'
#manila_glusterfs_target:
#manila_glusterfs_mount_point_base:
################################
# Swift - Object Storage Options
################################
# Swift expects block devices to be available for storage. Two types of storage
# are supported: 1 - storage device with a special partition name and filesystem
# label, 2 - unpartitioned disk with a filesystem. The label of this filesystem
# is used to detect the disk which Swift will be using.
# Swift support two matching modes, valid options are [ prefix, strict ]
#swift_devices_match_mode: "strict"
# This parameter defines matching pattern: if "strict" mode was selected,
# for swift_devices_match_mode then swift_device_name should specify the name of
# the special swift partition for example: "KOLLA_SWIFT_DATA", if "prefix" mode was
# selected then swift_devices_name should specify a pattern which would match to
# filesystems' labels prepared for swift.
#swift_devices_name: "KOLLA_SWIFT_DATA"
# Configure swift upgrade option, due to currently kolla support
# two upgrade ways for swift: legacy_upgrade and rolling_upgrade
# The variable "swift_enable_rolling_upgrade: yes" is meaning rolling_upgrade
# were enabled and opposite
# Rolling upgrade were enable by default
#swift_enable_rolling_upgrade: "yes"
###################################
# VMware - OpenStack VMware support
###################################
#vmware_vcenter_host_ip:
#vmware_vcenter_host_username:
#vmware_vcenter_host_password:
#vmware_datastore_name:
#vmware_vcenter_name:
#vmware_vcenter_cluster_name:
############
# Prometheus
############
#enable_prometheus_server: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_haproxy_exporter: "{{ enable_haproxy | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_mysqld_exporter: "{{ enable_mariadb | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_node_exporter: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_cadvisor: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_fluentd_integration: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool and enable fluentd | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_memcached: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_alertmanager: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_alertmanager_external: "{{ enable_prometheus_alertmanager | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_ceph_mgr_exporter: "no"
#enable_prometheus_openstack_exporter: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_elasticsearch_exporter: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool and enable_elasticsearch | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_blackbox_exporter: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_libvirt_exporter: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool and enable_nova | bool and nova_compute_virt_type in ['kvm', 'qemu'] }}"
#enable_prometheus_etcd_integration: "{{ enable_prometheus | bool and enable_etcd | bool }}"
#enable_prometheus_msteams: "no"
# The labels to add to any time series or alerts when communicating with external systems (federation, remote storage, Alertmanager).
# prometheus_external_labels:
# <labelname>: <labelvalue>
# By default, prometheus_external_labels is empty
#prometheus_external_labels:
# List of extra parameters passed to prometheus. You can add as many to the list.
#prometheus_cmdline_extras:
# List of extra parameters passed to cAdvisor. By default system cgroups
# and container labels are not exposed to reduce time series cardinality.
#prometheus_cadvisor_cmdline_extras: "--docker_only --store_container_labels=false --disable_metrics=percpu,referenced_memory,cpu_topology,resctrl,udp,advtcp,sched,hugetlb,memory_numa,tcp,process"
# Extra parameters passed to Prometheus exporters.
#prometheus_blackbox_exporter_cmdline_extras:
#prometheus_elasticsearch_exporter_cmdline_extras:
#prometheus_haproxy_exporter_cmdline_extras:
#prometheus_memcached_exporter_cmdline_extras:
#prometheus_mysqld_exporter_cmdline_extras:
#prometheus_node_exporter_cmdline_extras:
#prometheus_openstack_exporter_cmdline_extras:
# Example of setting endpoints for prometheus ceph mgr exporter.
# You should add all ceph mgr's in your external ceph deployment.
#prometheus_ceph_mgr_exporter_endpoints:
# - host1:port1
# - host2:port2
#########
# Freezer
#########
# Freezer can utilize two different database backends, elasticsearch or mariadb.
# Elasticsearch is preferred, however it is not compatible with the version deployed
# by kolla-ansible. You must first setup an external elasticsearch with 2.3.0.
# By default, kolla-ansible deployed mariadb is the used database backend.
#freezer_database_backend: "mariadb"
##########
# Telegraf
##########
# Configure telegraf to use the docker daemon itself as an input for
# telemetry data.
#telegraf_enable_docker_input: "no"
##########################################
# Octavia - openstack loadbalancer Options
##########################################
# Whether to run Kolla Ansible's automatic configuration for Octavia.
# NOTE: if you upgrade from Ussuri, you must set `octavia_auto_configure` to `no`
# and keep your other Octavia config like before.
#octavia_auto_configure: yes
# Octavia amphora flavor.
# See os_nova_flavor for details. Supported parameters:
# - flavorid (optional)
# - is_public (optional)
# - name
# - vcpus
# - ram
# - disk
# - ephemeral (optional)
# - swap (optional)
# - extra_specs (optional)
#octavia_amp_flavor:
# name: "amphora"
# is_public: no
# vcpus: 1
# ram: 1024
# disk: 5
# Octavia security groups. lb-mgmt-sec-grp is for amphorae.
#octavia_amp_security_groups:
# mgmt-sec-grp:
# name: "lb-mgmt-sec-grp"
# rules:
# - protocol: icmp
# - protocol: tcp
# src_port: 22
# dst_port: 22
# - protocol: tcp
# src_port: "{{ octavia_amp_listen_port }}"
# dst_port: "{{ octavia_amp_listen_port }}"
# Octavia management network.
# See os_network and os_subnet for details. Supported parameters:
# - external (optional)
# - mtu (optional)
# - name
# - provider_network_type (optional)
# - provider_physical_network (optional)
# - provider_segmentation_id (optional)
# - shared (optional)
# - subnet
# The subnet parameter has the following supported parameters:
# - allocation_pool_start (optional)
# - allocation_pool_end (optional)
# - cidr
# - enable_dhcp (optional)
# - gateway_ip (optional)
# - name
# - no_gateway_ip (optional)
# - ip_version (optional)
# - ipv6_address_mode (optional)
# - ipv6_ra_mode (optional)
#octavia_amp_network:
# name: lb-mgmt-net
# shared: false
# subnet:
# name: lb-mgmt-subnet
# cidr: "{{ octavia_amp_network_cidr }}"
# no_gateway_ip: yes
# enable_dhcp: yes
# Octavia management network subnet CIDR.
#octavia_amp_network_cidr: 10.1.0.0/24
#octavia_amp_image_tag: "amphora"
# Load balancer topology options are [ SINGLE, ACTIVE_STANDBY ]
#octavia_loadbalancer_topology: "SINGLE"
# The following variables are ignored as along as `octavia_auto_configure` is set to `yes`.
#octavia_amp_image_owner_id:
#octavia_amp_boot_network_list:
#octavia_amp_secgroup_list:
#octavia_amp_flavor_id:
####################
# Corosync options
####################
# this is UDP port
#hacluster_corosync_port: 5405
##############
# etcd options
##############
# If `etcd_remove_deleted_members` is enabled, Kolla Ansible will automatically
# remove etcd members from the cluster that are no longer in the inventory.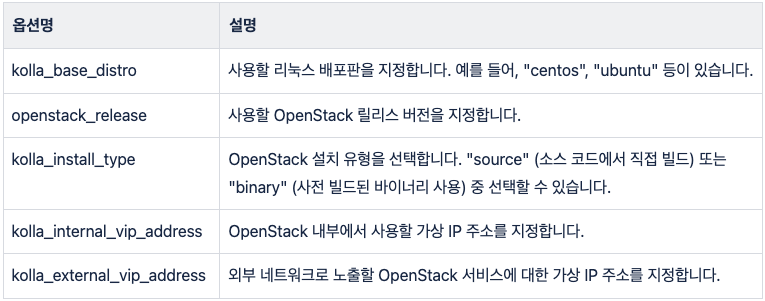



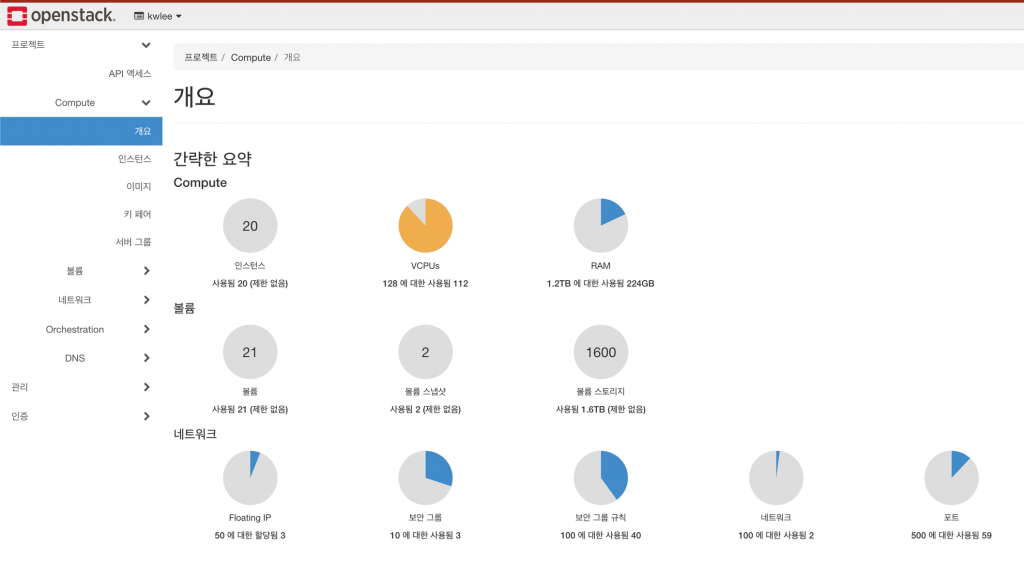
kolla-ansible prechecks 명령을 사용하여 배포 전에 시스템이 준비되었는지 확인합니다.kolla-ansible deploy -i /etc/kolla/inventory 명령을 실행하여 OpenStack 서비스들을 배포합니다. 이 과정에서 여러 Docker 컨테이너가 생성되고 구성됩니다.
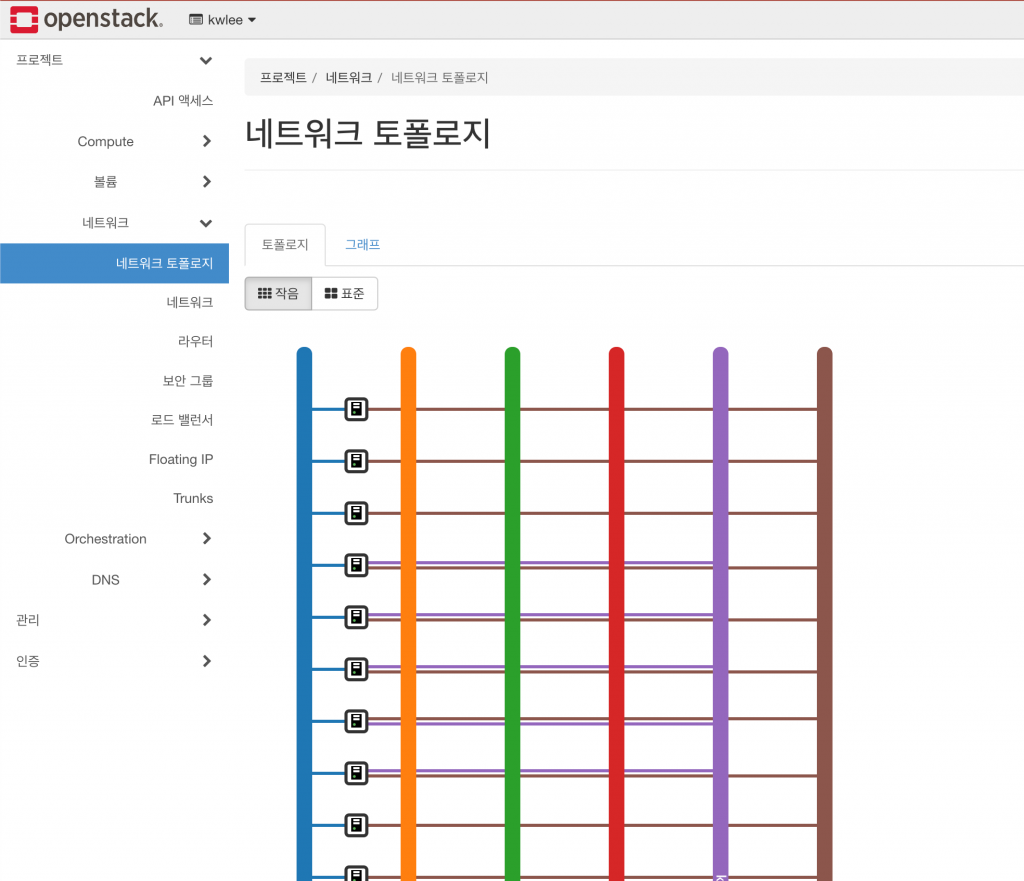
지금까지 Kolla-Ansible를 사용하여 OpenStack을 구축 해 보았습니다.
생각보다 쉽게 구축이 됬다고 느낄만큼 간단한 옵션조정을 통해 구축이 되었습니다.
물론 Kolla-Ansible은 OpenStack 의 구축을 위한 프로젝트여서 쉽게 보일 수 있습니다만은 기본적으로 Ansible의 Playbook과 다량의 서버들을 관리, 확인하는 Ansible을 사용하게 되므로 Ansible에 익숙해져야 하고, OpenStack의 구성요소에 익숙해져야 합니다.
오늘은 가볍게 개념과 활용 방법에 대해여 알아 보았다고 보시면 되겠습니다.
Kolla-Ansible을 이용하여 OpenStack을 구성한다는 것은 클러스터의 사이징, 스토리지, 네트워크, 가상화 모듈 등 다양한 요인을 이해하고 적절하게 옵션을 조절해야 합니다.
따라하면서 사용한 OpenStack 설치와는 많이 다를 수 있습니다. 따라서 구축하기 위해 많은 오픈스택에 대한 아키텍처 작업이 선행이 되어야 하며, 아키텍처를 확인 하는 방법으로 Kolla-Ansible을 활용하여 배포를 손쉽게 할 수 있습니다.
오픈소스컨설팅에서는 기술의 공유를 가장 큰 가치로 삼고 있습니다. 회사의 목표이기도 한 기술의 공유를 통해 같이 성장 했으면 합니다.
이번 블로그를 통해 Kolla-Ansible 그리고 OpenStack의 쉬운 설치를 경험하고 엔지니어 동료들에게 활용이 되었으면 합니다.
관련 글 더보기